Hot New Products Mild Steel Plate Size - Theoretical Knowledge of Wear-Resistant Steel Plate – XINXIN PENGYUAN
Hot New Products Mild Steel Plate Size - Theoretical Knowledge of Wear-Resistant Steel Plate – XINXIN PENGYUAN Detail:
The wear-resistant layer of the alloy is mainly chromium alloy, and other alloy components such as manganese, molybdenum, niobium and nickel are also added. The carbides in the metallographic structure are fibrous distribution, and the fiber direction is perpendicular to the surface. The micro hardness of carbide can reach above hv1700-2000, and the surface hardness can reach HRC58-62. Alloy carbides have strong stability at high temperature, maintain high hardness, and have good oxidation resistance. They can be used normally under 500 ℃.
The wear-resistant layer has narrow channels (2.5-3.5mm), wide channels (8-12mm), curves (s, w), etc; It is mainly composed of chromium alloy, and other alloy components such as manganese, molybdenum, niobium, nickel and boron are also added. The carbides in the metallographic structure are distributed in fibrous form, and the fiber direction is perpendicular to the surface. The carbide content is 40-60%, the microhardness can reach above hv1700, and the surface hardness can reach HRC58-62.
The wear-resistant steel plate alloy wear-resistant layer and the substrate are metallurgically bonded. Through special equipment and automatic welding process, the high hardness self protective alloy welding wire is uniformly welded on the substrate, and the composite layers are one to two or even multiple layers. During the composite process, uniform transverse cracks appear due to different alloy shrinkage ratios, which is the remarkable feature of wear-resistant steel plate.






Product detail pictures:
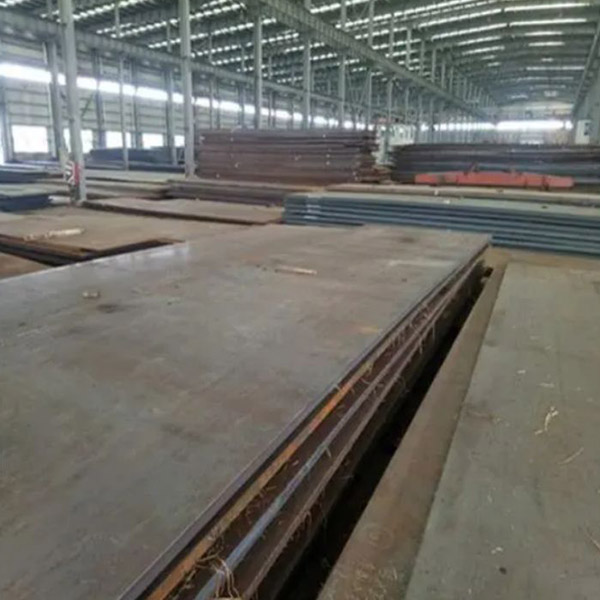






Related Product Guide:
We thinks what customers think, the urgency of urgency to act during the interests of a purchaser position of theory, allowing for much better good quality, lower processing costs, prices are extra reasonable, won the new and old buyers the support and affirmation for Hot New Products Mild Steel Plate Size - Theoretical Knowledge of Wear-Resistant Steel Plate – XINXIN PENGYUAN , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: panama, French, London, Our products are exported worldwide. Our customers are always satisfied with our reliable quality, customer-oriented services and competitive prices. Our mission is "to continue to earn your loyalty by dedicating our efforts to the constant improvement of our products and services in order to ensure the satisfaction of our end-users, customers, employees, suppliers and the worldwide communities in which we cooperate".
On this website, product categories is clear and rich, I can find the product I want very quickly and easily, this is really very good!